- Accueil>
- Actualités>
- Etude du CRIIGEN sur la toxicité des OGM : Qui croire ? Que croire ??
Etude du CRIIGEN sur la toxicité des OGM : Qui croire ? Que croire ??

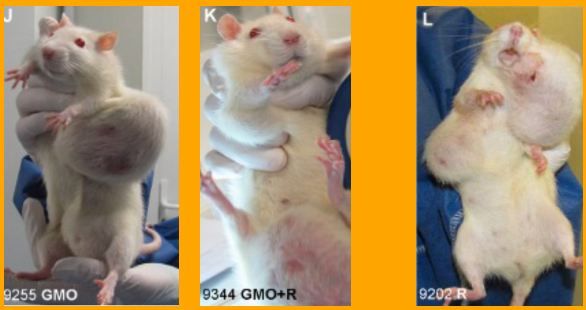
Suite à l’étude toxicologique réalisée par le Professeur Séralini de l'Université de Caen sur un échantillon de 200 rats qui montre une surmortalité des animaux nourris avec des OGM sur une longue durée (2 ans), José Bové, vice-Président de la commission de l'Agriculture et du Développement Rural au Parlement européen a demandé à la Commission européenne de suspendre immédiatement les autorisations de mise en culture et d'importation d'OGM. De leur côté, les experts de l’Association Française des Biotechnologies Végétales (AFBV) qui réunit des scientifiques des biotechnologies signalent que, contrairement à ce qui est affirmé, cette étude du CRIIGEN n’est pas la première à avoir évaluer les effets a long terme des OGM sur la santé. Ils rappellent qu’il existe de nombreuses études toxicologiques qui ont évalué les effets à long terme des OGM sur la santé des animaux dont une étude à 3 ans sur les porcs. Et que ces études réalisées sur des rats, des porcs mais aussi sur d’autres animaux par des chercheurs d’horizons différents n’ont jamais révélé d’effets toxiques des OGM. Des chercheurs apportent également un bémol à l'étude du CRIIGEN en révelant que la race de rats soumis à l'expérimentation est particulièrement sensible au cancer. La bataille entre pro et anti OGM n’est pas prête de s’arrêter...
Pour José Bové, vice-Président de la commission de l'Agriculture et du Développement Rural au Parlement Européen, "l'étude du Professeur Séralini du CRIIGEN (Comité de Recherche et d'Information Indépendantes sur le génie GENétique) souligne en particulier que les études réalisées jusqu'à présent sur une durée de 3 mois sur de faibles échantillons n'étaient pas en mesure de faire apparaître cette surmortalité".
Pour l'AFBV (l’Association Française des Biotechnologies végétales), ce que dit José Bové est faux puisque des études de longue durée (de 3 ans sur des porcs, donc des monogastriques comme l'Homme), ont été menées. Par ailleurs, ces études ont prouvé l'inocuité des OGM sur la santé des porcs.
On peut aussi s'étonner de la façon dont le CRIIGEN a communiqué sur cette étude car pour le moment nul n'a eu accès aux résultats et au protocole de l'étude. Toutes les réactions que ce soient celle de José Bové, du parti Europe Ecologie-Les Verts (EELV) ont été faites à partir du communiqué de presse diffusé par le CRIIGEN. Sommes-nous encore en démocratie ou jugeons-nous coupables les individus et les technologies par anticipation sans en avoir pris la mesure entière?
L'AFBV envoie également à qui le demande la liste des expérimentations à court terme (3 mois), moyen terme et long terme (3 ans) effectuées sur des animaux à qui l'on a donné de la nourriture OGM. L'ayant reçu, je me permets de la publier:
Bibliography long term experiments with GM crops
Klaus Ammann, from Web of Science and other sources, 20120919
Ammann, K. (20120919)
Long Term Experiments related to Agriculture, including abstracts. In ASK-FORCE, Vol. 14, pp. 111p. Klaus Ammann, Neuchatel http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Ammann-Long-Term-Bibl-abstracts-20120919.pdf
Bartsch, D., Hans-Jörg Buhk, Karl-Heinz Engel, Christoph Ewen, Gerhard Flachowsky, Achim Gathmann, Petra Heinze, Christiane Koziolek, Georg Leggewie, Anke Meisner, Gerd Neemann, Ulli Rees, Andrea Scheepers, Stefanie Schmidt, Elisabeth Schulte, Kristina Sinemus, & Anja Vaasen (2007)
Long-term effects of genetically modified (GM) crops on health and the environment (including biodiversity), Final Report, Federal Office of Consumer Protection of Food Safety, Berlin, Department of Food and Nutrition, TUM, Munic, team-ewen, Darmstadt, Genius GmbH, Darmstadt, Institute of Animal Nutrition, Friedrich Löffler Institute, Braunschweig, BLaU - Consultancy on Landscape Ecology and Environmental Studies, Göttingen pp 133 BEETLE Brussels (Report) http://ec.europa.eu/food/food/biotechnology/reports_studies/docs/lt_effects_report_en.pdf AND http://www.ask- force.org/web/Regulation/BEETLE-Report-Long-Term-2007.pdf
Breckling Broder, Reuter Hauke, & Verhoeven Richard, eds. (2008)
Implications of GM-Crop Cultivation at Large Spatial Scales, Proceedings of the GMLS-Conference 2008 in Bremen, Vol. 18, pp 180, Breckling Broder, Peter Lang, Bremen and Frankfurt am Main, Berlin, Bern, Bruxelles, New York, Oxford, Wien,,
http://www.peterlang.com/LOCALPDF/Buecher/BookDetail_58939.pdf?CFID=26834529&CFTOKEN=33100549
Castaldini, M., Turrini, A., Sbrana, C., Benedetti, A., Marchionni, M., Mocali, S., Fabiani, A., Landi, S., Santomassimo, F., Pietrangeli, B., Nuti, M.P., Miclaus, N., & Giovannetti, M. (2005)
Impact of Bt corn on rhizospheric and on beneficial mycorrhizal symbiosis and soil eubacterial communities iosis in experimental microcosms. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 11, pp 6719-6729 ://000233225000033 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Castaldini-Impact-Bt-Rhizospheric-2005.pdf
Catt, J. & Henderson, I. (1993)
Rothamsted Experimental Station – 150 Years of Agricultural Research
http://pub2web.metastore.ingenta.com/ns/"> The Longest Continuous Scientific Experiment? Interdisciplinary Science Reviews, 18, 4, pp 365-378 http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/maney/isr/1993/00000018/00000004/art00010 AND http://dx.doi.org/10.1179/030801893789766609 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Catt-Rothamsted-Experimental- Station-Longest-1993.pdf
Craig, W., Tepfer, M., Degrassi, G., & Ripandelli, D. (2008)
An overview of general features of risk assessments of genetically modified crops. Euphytica, 164, 3, pp 853-880 http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9643-8 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Craig-Overview-Genreal-Features- 2008.pdf
Crawley, M. & Brown, S. (2004)
Spatially structured population dynamics in feral oilseed rape. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, 271, pp 1909–1916 http://www.journals.royalsoc.ac.uk/media/53F7YLTRVQ4Q54QMHQVL/Contributions/1/R/8/K/1R8KTGGXUP8AN0T5.pdf and http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Feral/Crawley-Spacially-Struct-2004.pdf and F1000-evaluation http://www.facultyof1000.com/article/nonpub49848/evaluation
Crawley, M.J. (1986)
Ecological Knowledge and Environmental Problem-Solving - Concepts and Case-Studies - Orians,Gh. Nature, 322, 6076, pp 219-219 http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Crawley-Committee-Ecology-1986.pdf
Crawley, M.J. (1986)
The Population Biology of Invaders. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B-Biological Sciences, 314, 1167, pp 711-731 ://A1986F345800014 AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Crawley-Population-Invaders-1986.pdf
Crawley, M.J. (1989)
Insect Herbivores and Plant-Population Dynamics. Annual Review of Entomology, 34, pp 531-564 ://A1989T004500024 NOT EZB, NOT NEBIS
Crawley, M.J., Brown, S.L., Hails, R.S., Kohn, D.D., & Rees, M. (2001)Biotechnology - Transgenic crops in natural habitats. Nature, 409, 6821, pp 682-683 http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Monitoring/Crawley-Natural-2001.pdf
Flachowsky, G., Halle, I., & Aulrich, K. (2005)
Long term feeding of Bt-corn - a ten-generation study with quails. Archives of Animal Nutrition, 59, 6, pp 449-451 ://000233641600008 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Feed/Flachowsky-Long-Term-Feedingstudy-2005.pdf
Flachowsky, G. & Wenk, C. (2010)
The role of animal feeding trials for the nutritional and safety assessment of feeds from genetically modified plants - Present stage and future challenges. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 19, 2, pp 149-170 ://WOS:000278973200001 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Feed/Flachovsky-Role-Animal-Feeding-2010.pdf
Fliessbach, A., Mader, P., Dubois, D., Gunst, L., Stauffer, W., Fried, P., Pfiffner, L., Alföldi, T., & Niggli, U. (2000)
Organic Farming enhances soil fertility and biodiversity, Research Institute of Organic Agriculture, Federal Research Station for Agroecology and Agriculture pp 16 Fibl Dossier 1, Frick, Switzerland (Report) http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Organic/DOC_slim.pdf AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Organic/DOC-slim-Slides.ppt
Head, G., Moar, M., Eubanks, M., Freeman, B., Ruberson, J., Hagerty, A., & Turnipseed, S. (2005)
A multiyear, large-scale comparison of arthropod populations on commercially managed Bt and non-Bt cotton fields. Environmental Entomology, 34, 5, pp 1257-1266 ://000232405800031AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Bt/Head-Multiyear-Nontarget-2005.pdf
Hommel, B. & Pallutt, B. (2002)
Evaluation of herbicide resistance against glufosinate in oilseed rape and maize in view of integrated plant protection - results of a long-term field experiment started in 1996 with a special view on field flora. Zeitschrift Fur Pflanzenkrankheiten Und Pflanzenschutz- Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, pp 985-994 ://000202836900128 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Hommel-Bewertung-Herbizidresistenz-2002.pdf
Ivarsson, K. (1990)
The Long-Term Soil Fertility Experiments in Southern Sweden. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, 40, pp 205-215 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00015129009438553 AND NEBIS 20120919
Koerschens Martin, Bus Elke, & Behrent Helga (1984)
Uebersicht ueber wichtige Dauerversuche der Welt. In Dauerfeldversuche der DDR, Berlin, pp. 217-230, Berlin http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Koerschens_Bus_Beherendt_1984_Uebersicht.pdf
Mattingly, G.E.G. (1957)
Effects of radioactive phosphate fertilizers on yield and phosphorus uptake by ryegrass in pot experiments on calcareous soils from Rothamsted. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 49, 02, pp 160-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600036133 AND NEBIS 20120919
Mattingly, G.E.G. & Johnston, A.E. (1976)
Long-Term Rotation Experiments at Rothamsted and Saxmundham-Experimental-Stations - Effects of Treatments on Crop Yields and Soil Analyses and Recent Modifications in Purpose and Design. Annales Agronomiques, 27, 5-6, pp 743-769 ://A1976DN70300014 AND NEBIS 20111201
Nickson, T.E. & Head, G.P. (1999)
Environmental monitoring of genetically modified crops. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 6, pp 101N-105N ://000084230600002 AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Nickson-Head-Monitoring.pdf
Pesaro, M. & Widmer, F. (2006)
Identification and specific detection of a novel Pseudomonadaceae cluster associated with soils from winter wheat plots of a long- term agricultural field experiment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 1, pp 37-43 ://000234662800003 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Pesaro-Identification-Detection-Longterm-2006.pdf
Ponti, L. (2005)
Transgenic Crops and Sustainable Agriculture in the European Context. Bulletin of Science Technology Society %R 10.1177/0270467605277292, 25, 4, pp 289-305 http://bst.sagepub.com/cgi/content/abstract/25/4/289 AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Ponti-Sustainable- 2005.pdf AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Ponti-Sustainable-2005-alpha.pdf
Poulton, P.R. (1996)
The Rothamsted long-term experiments: Are they still relevant? Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 76, 4, pp 559-571 http://dx.doi.org/10.4141/cjps96-103 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Poulton-Rothamstead-longterm-Relevant- 1996.pdf
Powlson, D.S. & Poulton, P.R. (1998)
Using the long―term experiments at rothamsted to address current agricultural and environmental issues. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 42, 6, pp 455-478 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03650349809385747 AND NEBIS 20120919
Rothamsted Research (2006) Guide to the classical and other long term experiments, dataset and sample archive Printed by Premier Printers Ltd, Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk. © Lawes Agricultural Trust Co. Ltd, Harpenden, Herts, AL5 2JQ, UK, IS: ISBN 0 9514456 9 3, pp 56
http://www.rothamsted.ac.uk/resources/LongTermExperiments.pdf
Rubaek, G.H. & Sibbesen, E. (1995)
Soil phosphorus dynamics in a long-term field experiment at Askov. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 20, 1, pp 86-92 http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00307847 AND NEBIS 20120919
Smith, P., Powlson, D., Glendining, M., & Smith, J.O. (1997)
Potential for carbon sequestration in European soils: preliminary estimates for five scenarios using results from long-term experiments. Global Change Biology, 3, 1, pp 67-79 http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.1997.00055.x AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Smith-Potential- CarbonSequestration-Longterm-1997.pdf
Snell, C., Bernheim, A., Berge, J.-B., Kuntz, M., Pascal, G., Paris, A., & Ricroch, A.E. (2012)
Assessment of the health impact of GM plant diets in long-term and multigenerational animal feeding trials: A literature review. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 50, 3–4, pp 1134-1148 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278691511006399 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Food/Snell- Assessment-Health-Impct-GM-2012.pdf
Snell Chelsea, Aude Bernheim, Jean-Baptiste Berge, Marcel Kuntz, Gerard Pascal, Alain Paris, & Ricroch Agnes E. (2011)
Assessment of the health impact of GM plant diets in long-term and multigenerational animal feeding trials: A literature review. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 0, pp http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278691511006399 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Chelsea- Assessment-Health-Longterm-2011.pdf
Trist, P.J.O. & Boyd, D.A. (1966)
The Saxmundham rotation experiments: rotation I. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 66, 03, pp 327-336 http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600063620 AND NEBIS 20120919
Viglizzo, E.F., Lertora, F., Pordomingo, A.J., Bernardos, J.N., Roberto, Z.E., & Del Valle, H. (2001)
Ecological lessons and applications from one century of low external-input farming in the pampas of Argentina. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 83, 1-2, pp 65-81 ://000166461200007 AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Viglizzo-Lessons-Pampas-2001.pdf
Wick, M. & Freier, B. (2000)
Long-term effects of an insecticide application on non-target arthropods in winter wheat - a field study over 2 seasons. Anzeiger Fur Schadlingskunde-Journal of Pest Science, 73, 3, pp 61-69 ://000087756700001 AND http://www.botanischergarten.ch/Longterm/Wick-Longterm-2000.pdf
Zueghart, W., Benzler, A., Berhorn, F., Sukopp, U., & Graef, F. (2008)
Determining indicators, methods and sites for monitoring potential adverse effects of genetically modified plants to the environment: the legal and conceptional framework for implementation. Euphytica, 164, 3, pp 845-852 http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9475-6 AND http://www.ask-force.org/web/Longterm/Zueghart-Determining-Indicators- Monitoring-2008.pdf
Images associée(s) à cette actualité :
Commentaire(s)
Autres articles sur AFBV





Les dernières actualités
Les actus des membres
Dernières vidéos
Les Guides conso
Tout savoir sur le contrôle obligatoire des pulvérisateurs
Le dispositif de contrôle périodique obligatoire des pulvérisateurs est effectif depuis le 1er janv (...)
Forum
Derniers posts
comment rencontre-t-on les filles ?
publié par moniccaa
Les Secrets pour Écrire des Articles Informés avec ChatGPT Français
publié par vikram
What do you know bitlife game?
publié par rakhisharmax